Alopecia areata is typically not dangerous, but it can become a psychological burden. In Germany, about 1.5 million people suffer from alopecia areata. Men are more frequently affected, with most of them being under the age of 40.
In this blog post, you will find everything you need to know about this form of hair loss, which often presents significant challenges to those affected. We will inform you about the causes and symptoms of alopecia areata and possible treatment methods. Additionally, we offer tips and tricks on how to cope with this condition and ways to boost your self-confidence. Our goal is to help you feel comfortable in your own skin and manage your daily life as best as possible despite alopecia areata.
What Causes Alopecia Areata?
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disorder where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys healthy hair follicles. It is believed that genetic factors may play a role in the development of alopecia areata. The condition can also be triggered by stress, including emotional stress, physical trauma, and hormonal changes.
Other possible factors include infections, particularly fungal or viral infections like the Epstein-Barr virus or herpes simplex virus. Chemotherapy and radiation therapy can also lead to alopecia areata.
The exact cause of alopecia areata is still unknown. Research is ongoing in this field, and there are many theories about what causes this condition. Each case is individual, and treatment can vary depending on the cause of the hair loss.
If you notice symptoms of alopecia areata, you should consult a dermatologist or hair disease specialist.
Symptoms of Alopecia Areata
The symptoms of alopecia areata are clear and easy to recognize. The affected areas on the scalp are round or oval, with diameters ranging from a few millimeters to several centimeters. The skin in these areas is smooth and shows no signs of inflammation or scaling.
The affected areas can appear singly or in multiples and can be located anywhere on the scalp. In some cases, other body hair, such as eyebrows, eyelashes, or beard hair, can also be lost.
There are different forms of alopecia areata, varying in extent. The most common form affects only a few spots on the scalp and usually leads to complete hair loss in these areas. In rare cases, there can be complete loss of all scalp hair or even all body hair (alopecia areata universalis).
If you suspect you have alopecia areata, you should seek medical advice. An accurate diagnosis is essential for finding appropriate treatment and ruling out possible causes.
Diagnosing Alopecia Areata
The first step in diagnosing alopecia areata is to conduct a comprehensive medical history. The doctor will ask about your medical history and perform a thorough examination. Tests may include a skin biopsy from the affected area, which is crucial as it informs the doctor about the type of hair loss and helps consider the right treatment.
The next step involves conducting blood tests to rule out or confirm possible hormonal causes. The doctor may also recommend tests to identify infections or other diseases associated with hair loss.
Some patients may be diagnosed with hypothyroidism. If this is the case, it must be treated and regularly monitored to see if symptoms improve. In other cases, psychological stress or stress may be the cause of hair loss; in such cases, it is advisable to seek professional help.
Diagnosing alopecia areata often requires multiple tests and examinations, as well as a thorough medical history. Given the problem’s complexity, always consult your doctor and report all symptoms so they can help you. This is the only way to ensure you receive the correct diagnosis, treatment, and achieve healthy results.
Treatment Options for Alopecia Areata
There are various treatment options, depending on the severity of the condition and individual needs.
One option is the local application of corticosteroid preparations on the affected skin area. These can suppress inflammation and the immune system, stimulating hair growth again. Another option is therapy with immunomodulating drugs like cyclosporine or tofacitinib. These specifically target the body’s immune system and can stop hair loss.
External stimulation of hair follicles can also help trigger hair growth. This can involve special laser or light treatments, microneedling therapies, and minoxidil. A targeted change in diet can also provide the body with essential nutrients and promote hair growth.
How Long Does Alopecia Areata Last?
Alopecia areata can last for varying periods, depending on the condition’s severity and the individual healing process. For some, the bald spots may disappear on their own within weeks or months, while for others, hair loss may be permanent.
Early diagnosis and treatment increase the chances of a full recovery. However, there is no guarantee of successful healing, as alopecia areata often occurs spontaneously and unpredictably.
It’s important to remain patient and not get discouraged if hair loss persists longer than expected. A positive attitude and confidence in your body can help normalize hair growth again.
How to Prevent Alopecia Areata?
Taking specific measures is crucial to prevent alopecia areata. Firstly, maintain a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals. Regular scalp care can also minimize hair loss risk. Avoid aggressive shampoos or chemicals. Additionally, avoid unnecessary stress and allow yourself sufficient rest.
While there’s no guaranteed way to prevent alopecia areata, these preventive measures can help reduce the risk and improve scalp and hair well-being.
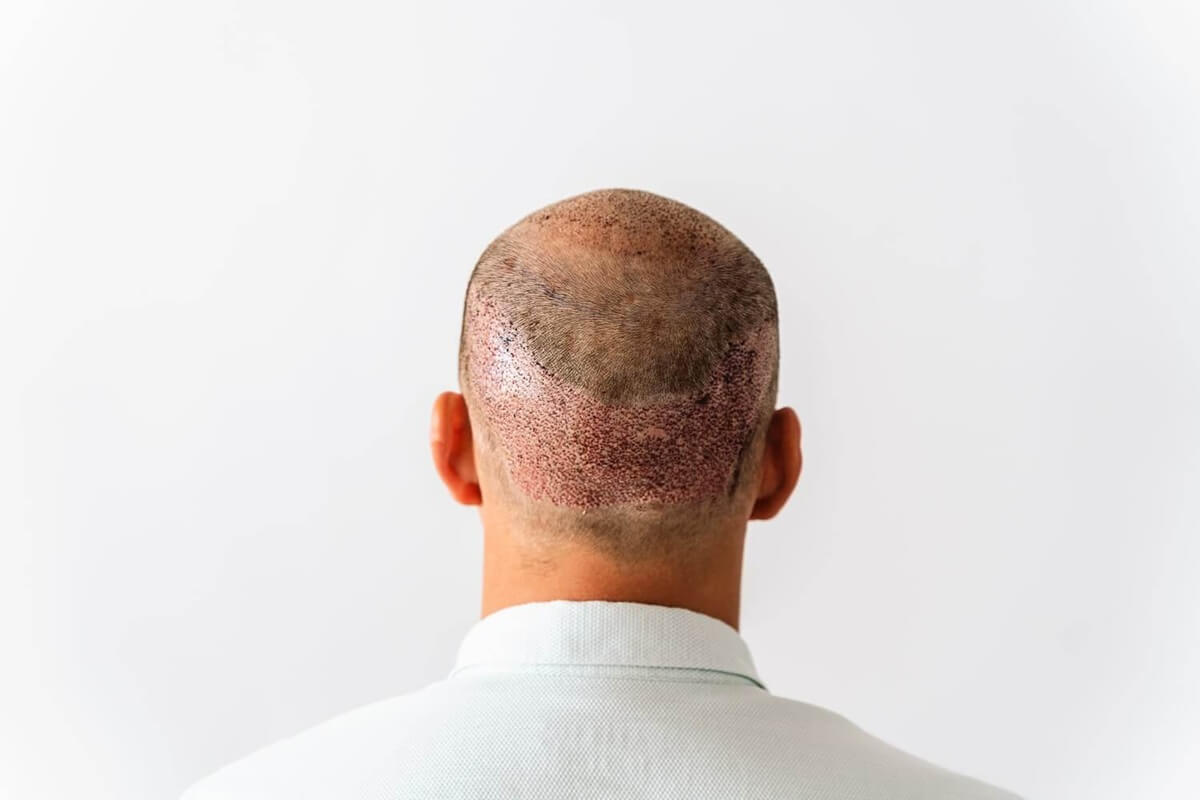
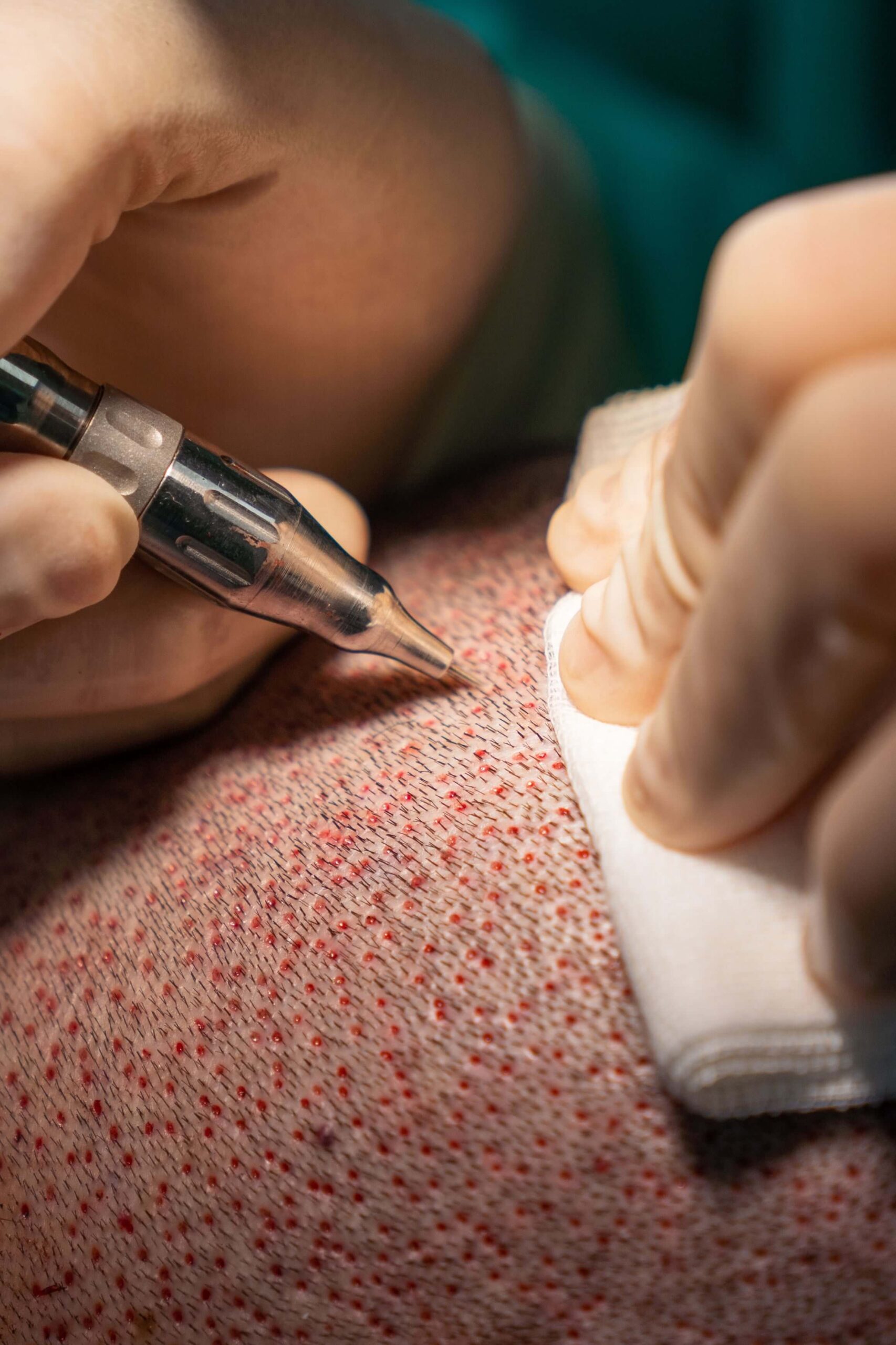
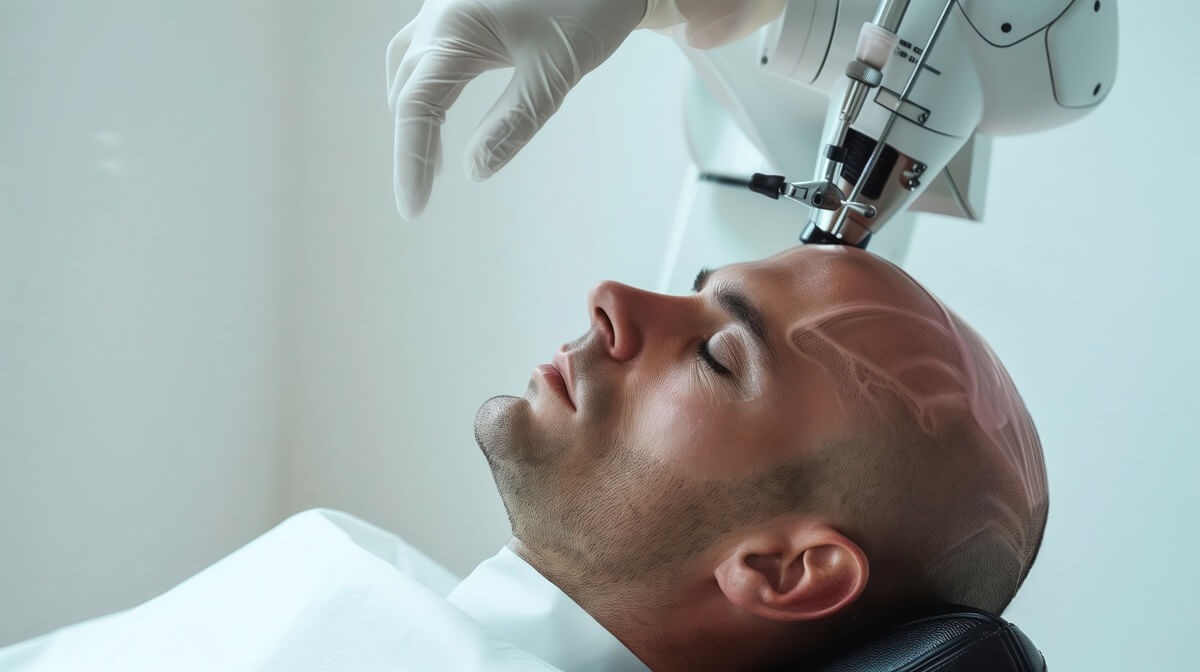
Is a Hair Transplant Suitable for Alopecia Areata?
A thorough examination of the individual case by an expert is always recommended before considering a hair transplant. Not every patient is a suitable candidate for this procedure. There must be enough donor hair to cover the bald spots, and the progression of alopecia areata must be halted.
Another crucial point is that hair transplant results for alopecia areata are less predictable than other forms of hair loss. The transplanted follicles may be attacked again by the immune system and fall out.
Overall, a hair transplant can be advisable under certain conditions for alopecia areata. However, it should always be decided on a case-by-case basis and involve a thorough pre-examination by an experienced doctor.
Conclusion
In conclusion, alopecia areata is a challenge but not the end of the world. There are various treatment options, and with the right treatment, most affected individuals can regain their hair. It is essential to consult a doctor early and not hesitate if the first signs appear. We hope this blog post has helped you learn more about alopecia areata.